What is the difference between PE (Portable Executable) and CIL (Common Intermediate Language)?
In .NET, C# code is compiled into Common Intermediate Language (CIL) by compiler at compile-time, then the CIL code will be compiled into machine code by Just-In-Time (JIT) compiler at runtime.
1. C# code life cycle:

1.1 C# code is human readable code
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace CsharpLibrary.Extensions
{
public static class EncodingExtension
{
public static string ToBase64(this string text)
{
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(text))
{
return text;
}
byte[] textAsBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(text);
return Convert.ToBase64String(textAsBytes);
}
}
}
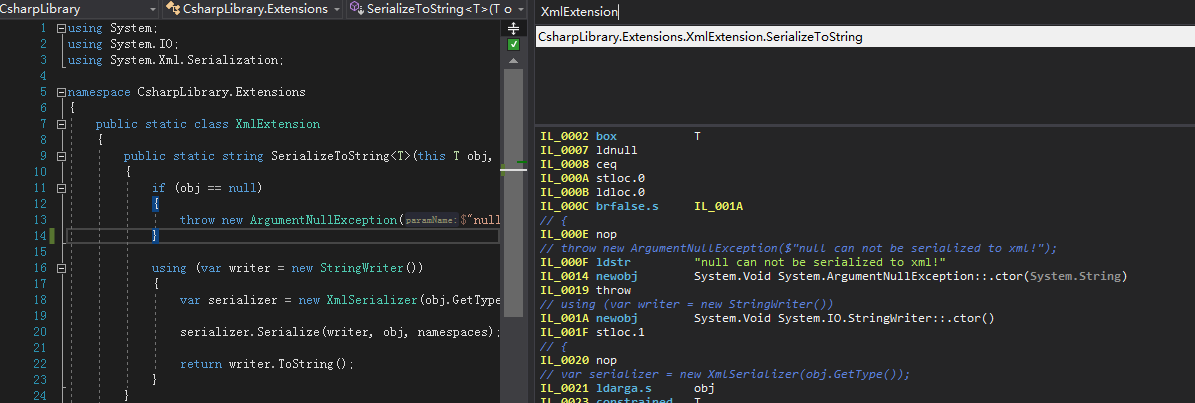
1.2 CIL is much less human readable
Common Intermediate Language is the object code or bytecode.
CIL is system architecture independant, which provides cross-platform support.
CIL is also called managed code because it’s managed by CLR (Common Language Runtime).
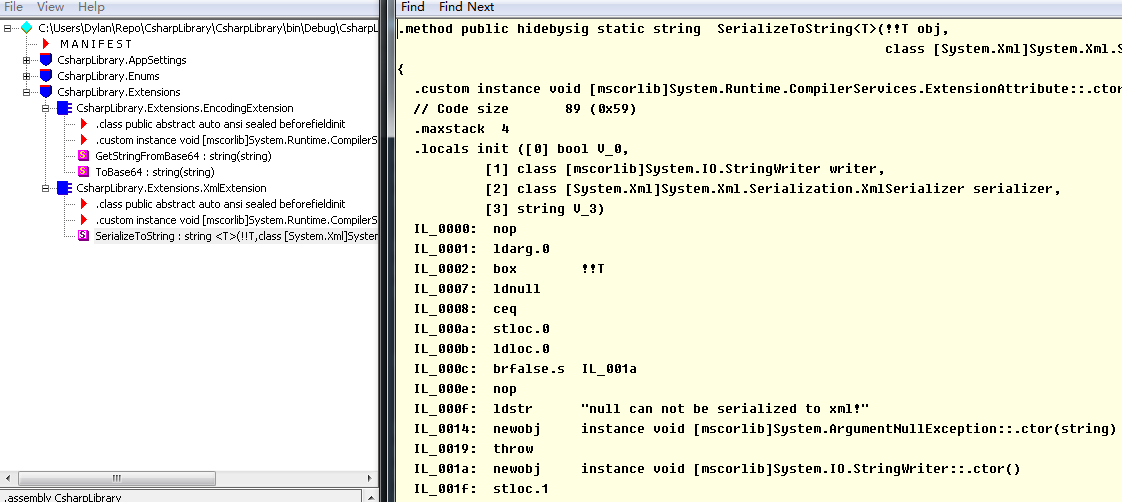
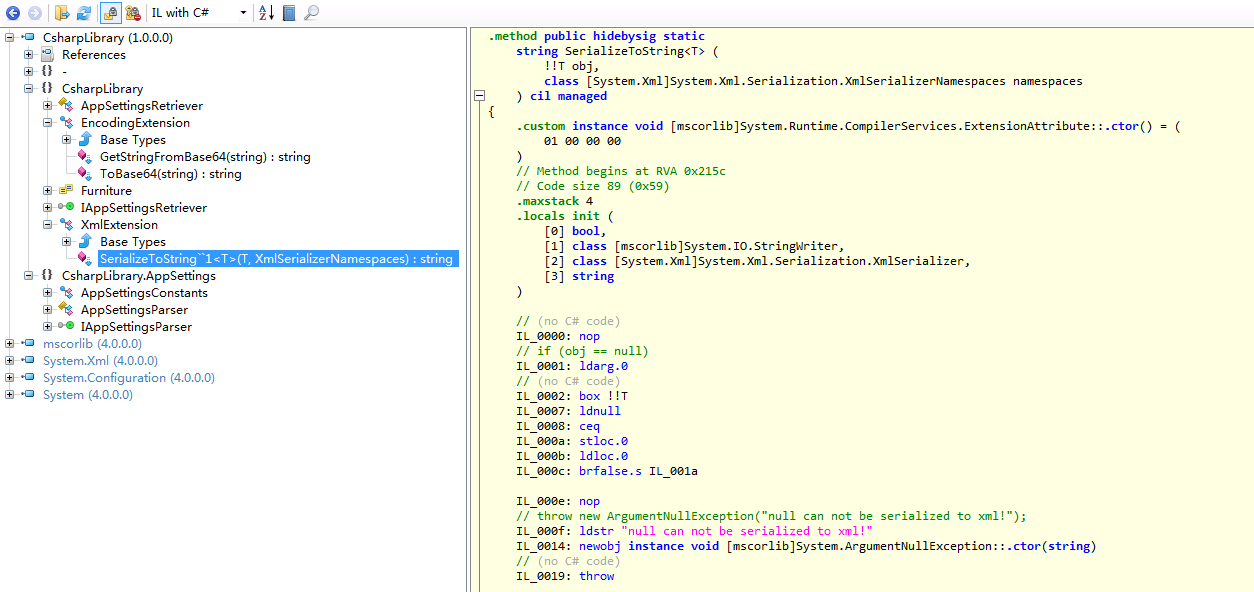
.class public auto ansi abstract sealed beforefieldinit CsharpLibrary.EncodingExtension
extends [mscorlib]System.Object
{
.custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.ExtensionAttribute::.ctor() = (
01 00 00 00
)
// Methods
.method public hidebysig static
string ToBase64 (
string text
) cil managed
{
.custom instance void [mscorlib]System.Runtime.CompilerServices.ExtensionAttribute::.ctor() = (
01 00 00 00
)
// Method begins at RVA 0x20f4
// Code size 39 (0x27)
.maxstack 2
.locals init (
[0] uint8[],
[1] bool,
[2] string
)
IL_0000: nop
IL_0001: ldarg.0
IL_0002: call bool [mscorlib]System.String::IsNullOrEmpty(string)
IL_0007: stloc.1
IL_0008: ldloc.1
IL_0009: brfalse.s IL_0010
IL_000b: nop
IL_000c: ldarg.0
IL_000d: stloc.2
IL_000e: br.s IL_0025
IL_0010: call class [mscorlib]System.Text.Encoding [mscorlib]System.Text.Encoding::get_UTF8()
IL_0015: ldarg.0
IL_0016: callvirt instance uint8[] [mscorlib]System.Text.Encoding::GetBytes(string)
IL_001b: stloc.0
IL_001c: ldloc.0
IL_001d: call string [mscorlib]System.Convert::ToBase64String(uint8[])
IL_0022: stloc.2
IL_0023: br.s IL_0025
IL_0025: ldloc.2
IL_0026: ret
} // end of method EncodingExtension::ToBase64
} // end of class CsharpLibrary.EncodingExtension
How to check CIL code?
There are several ways to check CIL code:
- Ildasm.exe Ildasm.exe is a tool provided by .NET framework. You can find it in .NET framework folder and Microsoft SDK folder on Windows system.
- ILSpy ILSpy is a open source project on Github to view CIL in a more elegant way than Ildasm.
- Msiler Msiler is a visual studio plugin to view CIL on live mode.
You can download its different versions:
Msiler for Visual studio 2012/2013/2015
OpCode (Operation Code)
CIL is not Assembly Language, even if it has OpCodes. But they are quite different from Assembly Language. Because it has only “add” operator, and manipulate only the stack.
Here “nop”, “ldarg”, “stloc” etc are all OpCode.
| OpCode | Meaning |
|---|---|
| nop | No operation |
| ldarg.0 | Load argument 0 on the stack |
| stloc.0 | Pop value from stack to local variable 0 |
| ldloc.0 | Load local variable 0 onto the stack |
| call bool [mscorlib]System.String::IsNullOrEmpty(string) | Call a method |
Check more about OpCode: What is OpCode in CIL?
1.3 Machine code is the code read by CPU
Machine code can be generated:
- By JIT (Just-In-Time) compiler JIT compiler compile CIL code into CPU instruction code at runtime
- By NGEN (Native Image Generator) NGEN will compile assembly or executable into native image at installation
2. What is PE (Portable Executable)?
Portable Executable is the executable format of object file or byte code on Windows systems. And CIL is the object file in C#, F#, C++ or VB.
Portable Executable format on Windows system are mostly .exe and .dll.
The Common Object File Format (COFF) is a format for executable, object code, and shared library computer files used on Unix systems. COFF is now replaced by Executable and Linkable Format (ELF) in Unix systems.
2.1 Build
When you build a project to a .dll or .exe:
For projects up to .NET 4.5.1, use MSBuild.exe in .NET framework folder:
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319>
MSBuild.exe "C:\Users\Dylan\Repo\CsharpLibrary\CsharpLibrary\CsharpLibrary.csproj"
I have some C# 6 syntax in the CsharpLibrary project, and when I build it, I’ve got the following error: Error CS1056: Unexpected character ‘$’ So I have to build the project with MSBuild.exe in
For projects from .NET 4.5.2, use MSBuild.exe in Visual Studio folder :
C:\Program Files (x86)\MSBuild\14.0\Bin>
MSBuild.exe "C:\Users\Dylan\Repo\CsharpLibrary\CsharpLibrary\CsharpLibrary.csproj"
csc.exe -target:library
MSBuild.exe use csc.exe to build C# project, the difference is MSBuild.exe will find all the related project references, but you have to manage them when using csc.exe
How to check PE ? You can check PE code by tools: